Myel: The Backbone of Medical and Biological Vocabulary
Byline: Explore the profound significance of the root "myel," derived from the Greek word for "marrow." From describing protective layers in the nervous system to diseases affecting bone marrow, "myel" forms the basis of crucial medical terms like "myelin" and "myeloma," revealing its indispensable role in health and science.
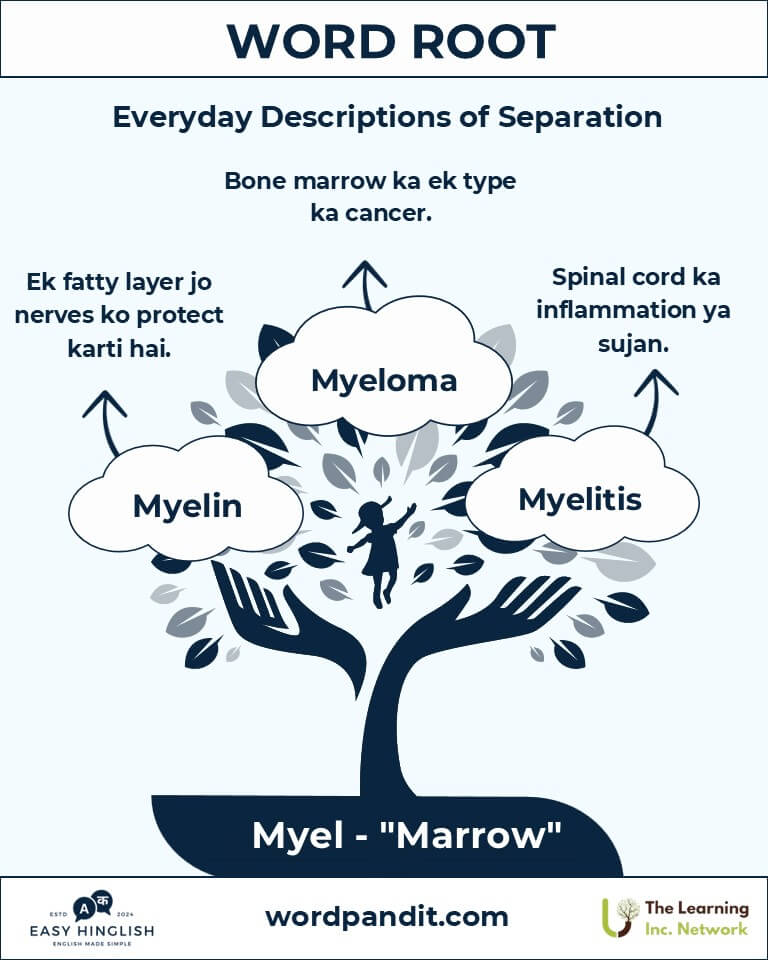
Table of Contents
- Introduction: The Vital Core of "Myel”
- Etymology and Historical Journey
- Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Myel
- Common Myel-Related Terms
- Myel Through Time
- Myel in Specialized Fields
- Illustrative Story: Myel in Action
- Cultural Significance of the Myel Root
- The Myel Family Tree
- FAQs About the Myel Word Root
- Test Your Knowledge: Myel Mastery Quiz
- Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Myel
Introduction: The Vital Core of "Myel"
The root "myel" means "marrow" (गूदा). It plays a critical role in medical terminology, representing the importance of bone marrow and spinal cord in human health.
- Bone marrow: Produces blood cells essential for survival.
- Spinal cord: Facilitates signal transmission between the brain and body.
Etymology and Historical Journey
The root "myel" is derived from the Greek word "myelos," meaning "soft tissue inside bones." Over time, its applications expanded to include neurological and hematological contexts. Advances in microscopic imaging during the 19th and 20th centuries further enriched this root's significance.
Mnemonic: Unlocking the Power of Myel
Picture a tree with roots representing marrow—providing strength and growth to the tree.
Mnemonic Device: "Myel means marrow—core of strength in body and brain."
Common Myel-Related Terms
- Myelin: A fatty sheath protecting nerve fibers and aiding signal transmission.
- Example: "Demyelination in multiple sclerosis disrupts nerve function."
- Myeloma: A type of cancer affecting bone marrow's plasma cells.
- Example: "Multiple myeloma weakens bones and compromises immunity."
- Myelitis: Inflammation of the spinal cord, causing pain and paralysis.
- Example: "Transverse myelitis can result in sensory and motor loss."
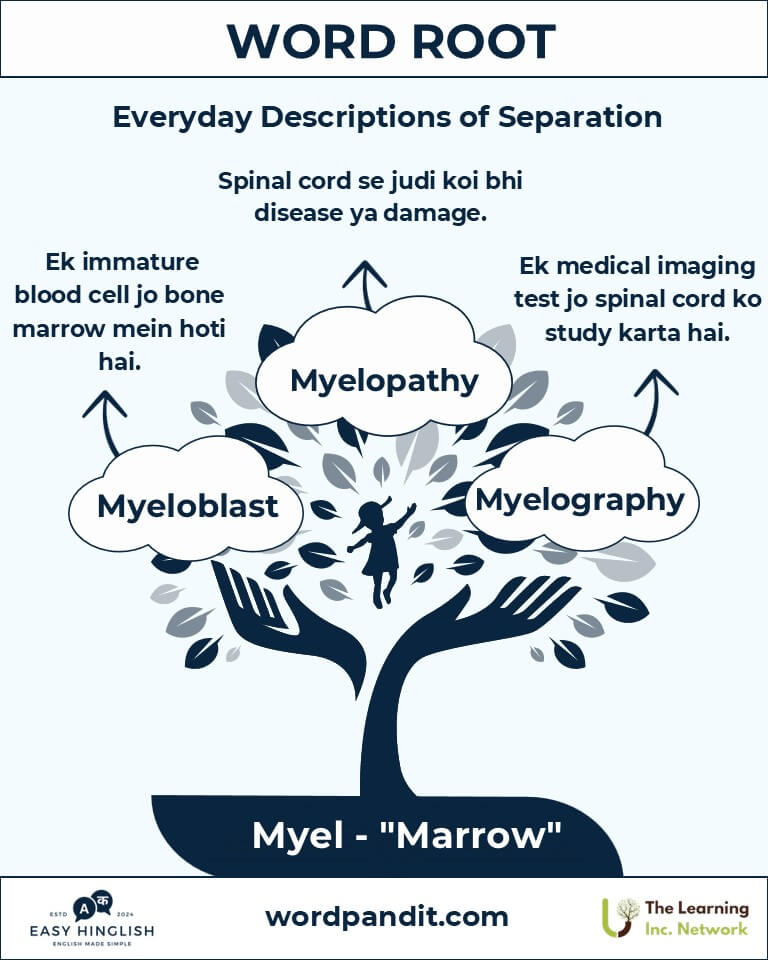
- Myeloblast: An immature blood cell found in bone marrow.
- Example: "Uncontrolled myeloblast growth is observed in leukemia."
Myel Through Time
- Ancient Understanding: Greek anatomists considered marrow as the "life center" essential for vitality.
- Modern Adaptation: Terms like "myelin sheath" and "bone marrow transplantation" highlight its importance in science.
- Future Focus: Therapies for neurodegenerative diseases like multiple sclerosis are being developed.
Myel in Specialized Fields
- Neurology: Study of myelin in disorders like multiple sclerosis.
- Hematology: Research on myeloblasts for diagnosing and treating blood cancers.
- Oncology: Advancements in immunotherapy for treating myeloma.
Illustrative Story: Myel in Action
Dr. Patel, a neurologist, treated a patient named Lily diagnosed with multiple sclerosis. Using advanced imaging, he identified her myelin degeneration and initiated a remyelination therapy. This allowed Lily to resume her favorite hobby—hiking—showcasing the transformative power of "myel."
Cultural Significance of the Myel Root
The root "myel" symbolizes life’s core and resilience. Ancient cultures viewed marrow as a source of vitality, a perspective that remains relevant in modern medicine.
The Myel Family Tree
- Neuro-: Related to nerves.
- Example: Neuropathy (nerve dysfunction).
- Osteo-: Related to bones.
- Example: Osteomyelitis (bone marrow infection).
FAQs About the "Myel" Root
Q1: "Myel" ka kya matlab hai? (What does "Myel" mean?)
"Myel" comes from the Greek word "myelos," meaning "marrow" (गूदा). It is used in terms related to bone marrow and the spinal cord. (Myel Greek शब्द "myelos" से आया है, जिसका अर्थ है गूदा।)
Q2: Nervous system mein myelin ka role kya hai? (What is the role of myelin in the nervous system?)
Myelin is a fatty sheath that protects nerve fibers and helps in the efficient transmission of electrical signals. It enables coordination, reflexes, and sensory perception. (Myelin एक फैटी शीथ है जो नर्व फाइबर्स को प्रोटेक्ट करती है।)
Q3: Multiple myeloma kya hota hai? (What is multiple myeloma?)
Multiple myeloma is a type of cancer that affects plasma cells in the bone marrow. Symptoms include weakened immunity, anemia, and fragile bones. (Multiple myeloma एक प्रकार का कैंसर है जो बोन मैरो के प्लाज्मा कोशिकाओं को प्रभावित करता है।)
Q4: Transverse myelitis kya hai? (What is transverse myelitis?)
Transverse myelitis is inflammation of the spinal cord that can cause pain, sensory loss, or paralysis. (Transverse myelitis रीढ़ की हड्डी की सूजन है।)
Q5: Myeloblasts kya hote hain? (What are myeloblasts?)
Myeloblasts are immature blood cells found in the bone marrow that help produce white blood cells, crucial for immunity. (Myeloblasts अपरिपक्व रक्त कोशिकाएं हैं जो श्वेत रक्त कोशिकाएं बनाती हैं।)
Test Your Knowledge: Myel Mastery Quiz
1. "Myel" root ka matlab kya hai? ("What does the root 'Myel' mean?")
2. Kaunsa disease plasma cells ke cancer ko describe karta hai? ("Which disease describes cancer of plasma cells?")
3. Myelin kis cheez ko protect karta hai? ("What does myelin protect?")
4. Spinal cord ke inflammation ko kya kehte hain? ("What is inflammation of the spinal cord called?")
5. Myeloblasts ka primary function kya hota hai? ("What is the primary function of myeloblasts?")
Conclusion: The Living Legacy of Myel
The root "myel" provides insights into vital systems of life. Bone marrow and myelin are critical for producing blood cells and enabling nervous system functions, highlighting the enduring relevance of "myel."







